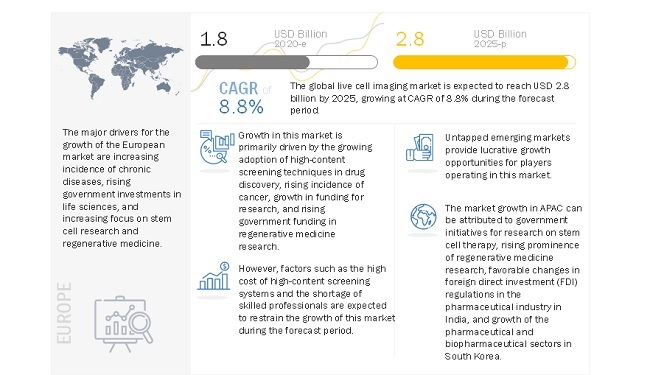
The global live cell imaging market size is expected to reach USD 2.8 billion by 2025 from an estimated value of USD 1.8 billion in 2020, growing at a CAGR of 8.8% during the forecast period. growing adoption of high-content screening techniques in drug discovery and rising incidence of cancer primarily drives the market for live cell imaging.
The growth in research funding and rising government funding and investment in regenerative medicine research will also support the market growth in the coming years. However, the high cost of high-content screening systems is limiting the overall adoption of these products.
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a tremendous increase in the burden on healthcare organizations across the globe. According to the WHO, as of September 29, 2020, there were 33,249,563 confirmed cases of COVID-19, including 1,000,040 deaths, with the highest number of deaths in the Americas, followed by Europe and Southeast Asia.
The normalization of the global economy will slowly increase the demand for live cell imaging systems in non-COVID-related research activity labs, leading to market growth from the first quarter of 2021. Furthermore, players operating in the market are altering their strategies, for both long-term and short-term growth, by tapping the research market and developing innovative products to combat the pandemic.
For More Information Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=163914483
To overcome these challenges, pharmaceutical companies are increasingly adopting high-content screening (HCS) cell-based assays for identifying the effects of toxicity in drug development studies (cell-based imaging enables the monitoring of drug toxicity mechanisms, such as oxidative stress, micronuclei, mitochondrial dysfunction, steatosis, and apoptosis).
The use of HCS makes the drug development process more time- and cost-efficient. Owing to these factors, the adoption of high-content screening for toxicity studies is expected to increase during the forecast period. This, in turn, is expected to drive market growth as live cell imaging is used in HCS to identify meaningful information from complex systems such as in vitro, in vivo, and ex vivo systems.
Academic research laboratories find it difficult to afford such high-priced instruments as they have restricted budgets. The high price of these instruments is also a concern for several pharmaceutical companies as they require multiple HCS systems in their R&D activities (thus increasing the total cost spent on these systems). In addition to the high procurement costs, the maintenance costs and several other indirect expenses increase the total cost of ownership of these instruments. This is one of the major factors limiting the adoption of live cell imaging instruments in clinical and research applications, especially in emerging countries.
The growing funding and investments in life science research, availability of highly skilled personnel, and a favorable regulatory environment are the other major factors supporting this trend. Moreover, currently, China has many CROs that provide preclinical and clinical research services to multinational pharmaceutical companies. The growth of preclinical/clinical research in China is expected to augment the demand for live cell imaging in the country in the coming years.