The emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic has changed the delivery of medical care across the world. The increased pressure due to the growing rate of hospitalization of COVID-19 patients had led to the re-profiling of many hospitals and departments for treating patients with COVID-19. Consequently, many elective surgeries were canceled or postponed worldwide to reserve or redirect the available limited capacities and resources (like hospital beds and patient care professionals) toward COVID-19 patient care.
In particular, the provision of ENT-related surgeries and services has been disproportionally affected due to the reallocation of intensive care resources. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), ENT clinics and audiology centers pose a medium-to-high risk for COVID-19 infection, considering the proximity, test set-up, and length of appointments. The fact that a majority of people who require audiology services (aged over 65 years) are also the ones at the highest risk of COVID-19 related mortality and morbidity, underscores the importance of reassessing how hearing care is delivered.
The outbreak of COVID-19 has led to an increase in the preference for remote monitoring. The crisis has ushered in a new era in the hearing healthcare space that requires a radical rethinking of service delivery in audiology. Low- and no-touch services are now necessary for audiology patients (who are typically at the highest risk for COVID-19 morbidity and mortality due to their advanced age).
For More Info, Download PDF Brochure @ https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNew.asp?id=198630754
Hearing aids market growth is driven by the technological advancements in hearing aids, growing prevalence of hearing loss, and the increasing adoption of smart hearing aids due to the rising incidence of noise-induced hearing loss.
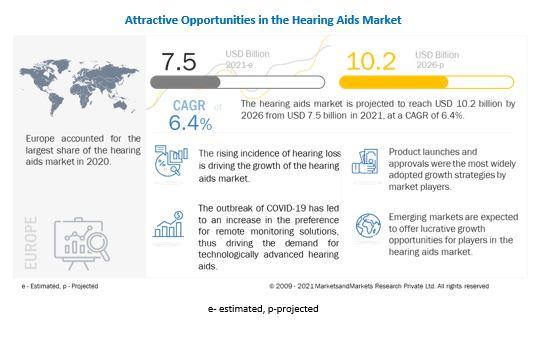
Globally, the rising incidence of hearing loss has made it extremely important to monitor and examine hearing functions. In children, untreated hearing loss negatively impacts language development, learning, and social engagement.
Similarly, older adults with hearing loss often have difficulty following day-to-day conversations. For people entering their retirement years, untreated hearing loss has been linked to several physical and psychological issues, ranging from cognitive decline and depression to an increased risk of trips and falls.
The dearth of skilled ENT surgeons in these countries is expected to limit the number of ENT procedures performed, including cochlear implantation, carried out per year despite the presence of a large target patient population base. This is a major challenge for the growth of the hearing aids market.
The hearing aids market is segmented into adults and pediatrics based on patient type. In 2020, the adult patients segment accounted for the largest share of the hearing aids market. The growing incidence of hearing loss among the adult population is driving the growth of this segment.