INTRODUCTION
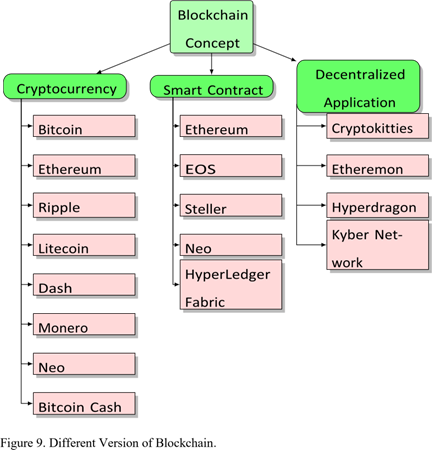
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed and immutable ledger that is secured by cryptographic hashing algorithms. The blockchain ledger has chained blocks of encryption and chronological data that are synchronized over the peer-to-peer network. The data is formed in blocks and each block is appended to its previous hash block. Blockchain initially stores the data in backwards linked blocks. It then verifies the blocks using a distributed consensus process to ensure security, data protection and transparency across the blockchain network. The best known and most widespread application of blockchain technology is Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency blockchain that has become the most promising technology for decentralized trust without third parties.
Autonomous data-driven industries have adopted blockchain technology as a mechanism for storing immutable data in a distributed and secure manner. Data security and data integrity was achieved through cryptocurrencies and smart contracts. The blockchain can be used as an additional layer in order to run the program on different machines in a consensus process. One of the reasons blockchain has led to cryptocurrency and smart contracts that make the critical requirement for data security and integrity. For general bytecode execution, orchestration for the global state can be achieved with distributed consensus, and blockchain technology is expected to evolve. Open access and transaction management in decentralized autonomous systems. It’s about the decentralization of assets in the financial sector, IoT, public services and decentralized applications, etc. Each new transaction is validated by a miner and recorded in a global ledger, each miner contributes his computing power to check the distributed ledger data blocks and can compete in a consensus process for the creation of the next new block added to the main chain. In the blockchain, there are two types of data in the data chain, kept in the blockchain and in the off-chain, which cannot be stored in the block to simplify the verification process. Blockchain uses a decentralized token system to authenticate the transfer of assets. In addition, a blockchain maintains an arbitrary order of transaction data records by cryptographically concatenating subsets of data records in the form of data blocks with their chronic predecessors. Transaction on the weakly synchronized network The authors have checked blockchain use cases and their adaptability in the IoT for integrity, anonymity, and interoperability. The authors have presented the blockchain as a solution for the security, data protection, and computing restrictions of various IoT devices.
Read more -- https://growinsd.com/blockchain-technology/