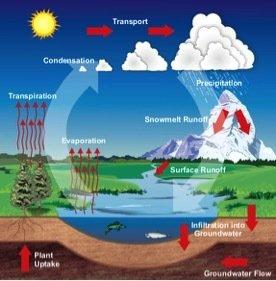
Evaporation is the process by which water changes from a liquid to a gaseous state, and this process plays a vital role in the weather and climate system. Here are a few key aspects of how evaporation affects the weather:
Precipitation Formation
Evaporation is an important part of the water cycle, transporting water from the surface to the atmosphere. When water evaporates into the atmosphere, it condenses under the right conditions to form clouds and eventually returns to the surface as precipitation (such as rain, snow, hail, etc.). This process is essential to maintaining the Earth's water balance.
Regulating Temperature
Evaporation is an endothermic process, meaning it requires the absorption of heat to convert liquid water into gaseous water vapor. This process absorbs heat from the surrounding environment, which has a cooling effect. For example, when sweat evaporates from the surface of human skin, it removes heat and makes people feel cooler. Similarly, large-scale evaporation processes, such as evaporation from the surface of the ocean, also have a regulating effect on local and global temperatures.
Affecting Humidity
Evaporation increases the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, which increases the humidity of the air. Humidity is an important parameter in weather forecasting. It not only affects people's comfort, but also has a direct impact on the formation of weather phenomena such as fog, dew and frost.
Promotes the formation of wind
During the evaporation process, water molecules change from liquid to gas, which needs to overcome the attraction between molecules. This process generates a certain amount of kinetic energy. When water vapor diffuses in the atmosphere, it drives the surrounding air to flow, thereby promoting the formation of wind. The formation of wind further promotes the transportation and distribution of water vapor, affecting weather patterns in a larger area.
Impact on climate
In the long run, the evaporation process has a profound impact on the climate system. For example, the ocean covers about 70% of the earth's surface, and its huge water reserves make seawater evaporation one of the main sources of global water cycle. Ocean evaporation not only affects humidity and precipitation in local areas, but also affects the climate of distant areas through water vapor transportation.
In summary, evaporation plays multiple key roles in the weather and climate system, from regulating temperature, affecting humidity to promoting precipitation and wind formation, all of which reflect its importance. Understanding the evaporation process and its impact is crucial for accurate weather forecasting and climate research.